[源码阅读] Mach-O 与 fishhook
fishhook 短小精湛的动态库函数hook库
![[源码阅读] Mach-O 与 fishhook](https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1572979124117-a72dfcb4014d?ixlib=rb-1.2.1&q=80&fm=jpg&crop=entropy&cs=tinysrgb&fit=max&ixid=eyJhcHBfaWQiOjExNzczfQ&w=1200)
__fishhook__ is a very simple library that enables dynamically rebinding symbols in Mach-O binaries running on iOS in the simulator and on device. This provides functionality that is similar to using [`DYLD_INTERPOSE`][interpose] on OS X. At Facebook, we've found it useful as a way to hook calls in libSystem for debugging/tracing purposes (for example, auditing(审查) for double-close (欺骗) issues with file descriptors (文件描述符)).
功能: (dyld interpose) 针对 动态库 来 hook c 函数的库. ps: 安卓可以查看 FastHook
不试用: 静态库的函数 hook, 或者严谨来说不能hook的是内部符号,能hook的是动态库的外部符号, 具体原因后面会讲解.
问题: 如果将来苹果更新动态链接器为 dyld 3.0, 那么该库会失效, 详情查看 fishhook with dyld 3.0
有关动态库插入的文档, 苹果官方的动态库插入宏 DYLD_INTERPOSE
#if !defined(_DYLD_INTERPOSING_H_)
#define _DYLD_INTERPOSING_H_
/*
* Example:
*
* static
* int
* my_open(const char* path, int flags, mode_t mode)
* {
* int value;
* // do stuff before open (including changing the arguments)
* value = open(path, flags, mode);
* // do stuff after open (including changing the return value(s))
* return value;
* }
* DYLD_INTERPOSE(my_open, open)
*/
#define DYLD_INTERPOSE(_replacement,_replacee) \
__attribute__((used)) static struct{ const void* replacement; const void* replacee; } _interpose_##_replacee \
__attribute__ ((section ("__DATA,__interpose"))) = { (const void*)(unsigned long)&_replacement, (const void*)(unsigned long)&_replacee };
#endif
这种动态库的函数 hook ,仅能用在 Mac 或者模拟器上使用, 在 iOS上是被禁止的, 所以可以用 fishhook 来代替
Mach-O
在了解 fishhook 的原理之前, 首先要了解可执行文件二进制的具体组成结构, 这才是真正的精华所在,只有明白了结构,才能明白 fishhook 为什么能处理动态库,而不能处理静态库的 c 函数.
Mac中的可执行文件分类如下:
- Mach-O 格式 MachOOverview
- 通用二进制格式
- 其是为了解决多架构的问题, 也称为 胖二进制格式, 它包含多个
Mach-O文件 - FAT_MAGIC: 0xcafebabe
- 其是为了解决多架构的问题, 也称为 胖二进制格式, 它包含多个
- 解释器脚本格式
查看格式类型可以使用 其二进制中的 Magic 数字
真正要了解的是 Mach-O 格式, 可以使用 MachOView 软件
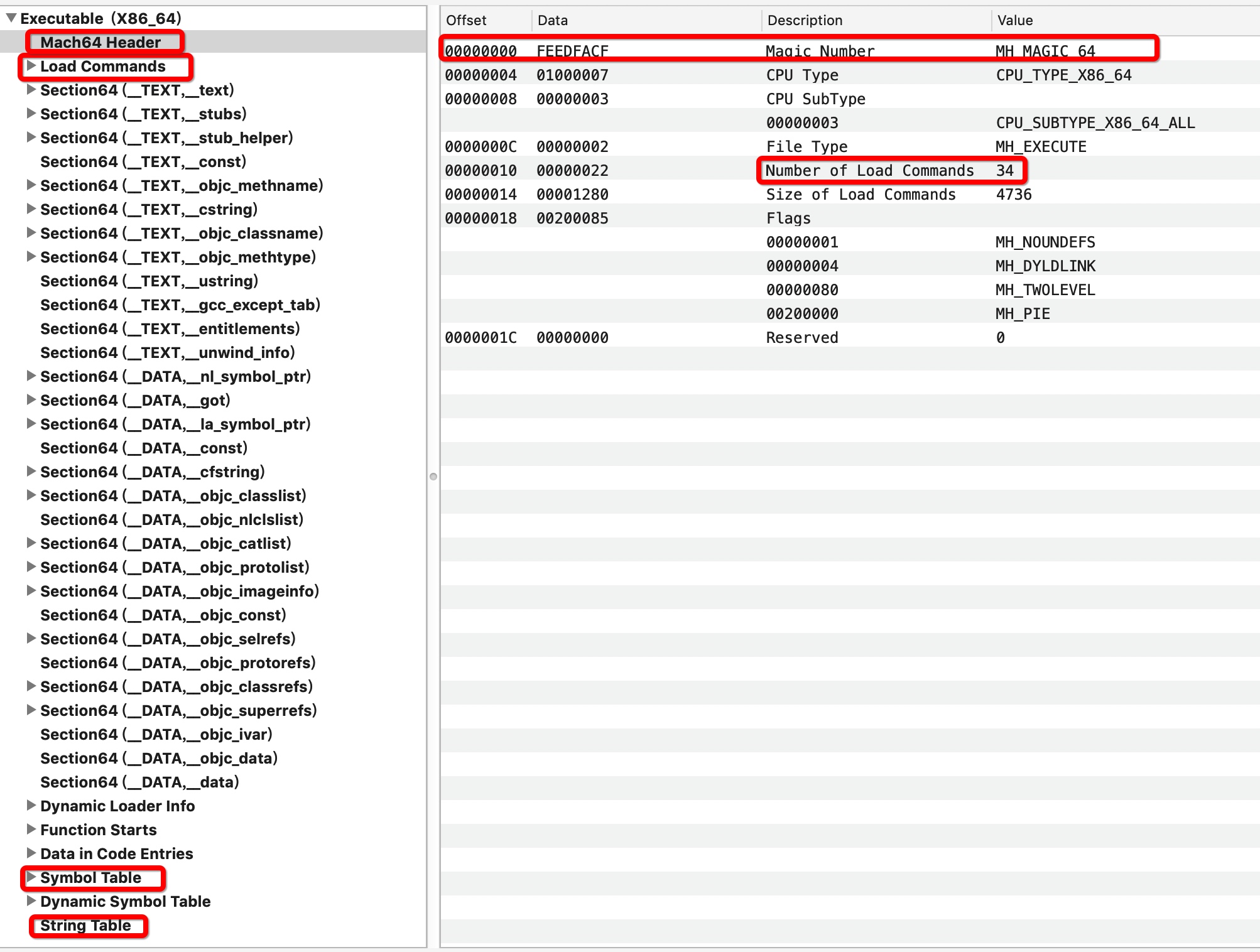
简单来说有如下组成:
- Mach Header
- Load Commands
2.1 描述了文件中数据的具体组织结构,不同的数据类型使用不同的加载命令表示
2.1 不同的动态库有不同的加载指令
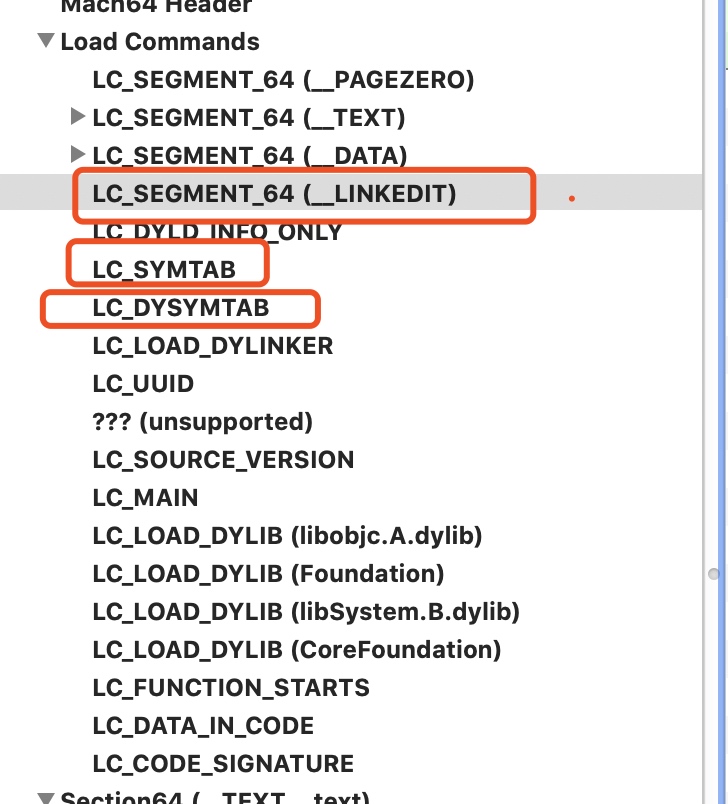
2.3 不同的command 有不同的长度 - 3个Segment { __TEXT __DATA __LINKEDIT }
这里要说的一点是, 图中可以看到, Section 后面有一些同样的标识 比如 __Text , __DATA等, 这些就是 Segment , 按照用途的不同,将内存分为不同的划分方式.
Segment 包含 多个 Section . 同一个 Segment 下的 Section,可以控制相同的权限,也可以不完全按照 Page 的大小进行内存对齐,节省内存空间。而对外整体暴露段,在装载程序的时候完整映射成一个vma,可以更好的做内存对齐
注意点: Segment 并不一定是由 Section 组成, 比如 __LINKEDIT.
mach_header
定义如下
/*
* The 64-bit mach header appears at the very beginning of object files for
* 64-bit architectures.
*/
struct mach_header_64 {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
uint32_t reserved; /* reserved */
};
/*
* The 32-bit mach header appears at the very beginning of the object file for
* 32-bit architectures.
*/
struct mach_header {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
| 字段 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| --- | --- |
| magic | 用于标识当前设备的是大端序还是小端序。如果是0xfeedfacf(MH_MAGIC_64)就是大端序,而0xcffaedfe(MH_CIGAM_64)是小端序,iOS系统上是小端序 |
| cputype | cpu类型,比如 CPU_TYPE_X86 和 CPU_TYPE_ARM64 ,具体查看 <mach/machine.h> |
| cpu_subtype_t | CPU子类型 如 CPU_SUBTYPE_MULTIPLE(大小端) , CPU_SUBTYPE_LITTLE_ENDIAN(小端), CPU_SUBTYPE_BIG_ENDIAN (大端) |
| filetype | 文件类型,共11种 ,不同文件类型其二进制内存分配不同, 比如 MH_DYLIB 为动态共享库. 具体请查看 <mach-o/loader.h> |
| ncmds | load command 的数量, 经常被用来遍历 command 使用 |
| sizeofcmds | load command的长度 |
| flags | 标记其权限与符号的一些信息,这个比较多 具体请查看 <mach-o/loader.h> |
| reserved | 暂未使用 |
也可以用 Hopper 查看更详细的信息
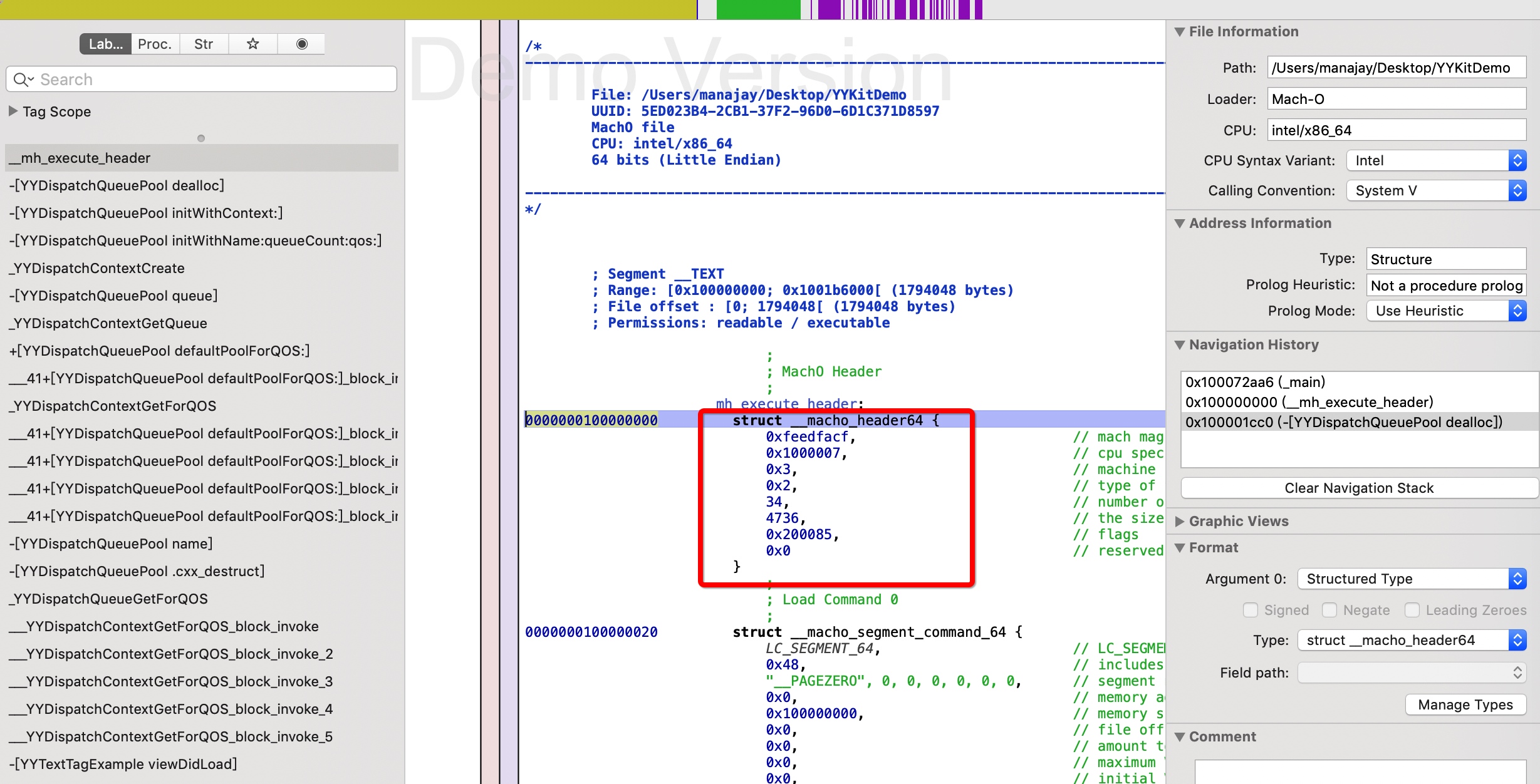
iOS 中使用静态库的时候,经常会遇到架构不支持的问题, 比如下面这个静态库就仅仅只能在模拟器使用
lipo -info xxx
Non-fat file: xxx is architecture: x86_64
如果是合成的多个架构,则是 fat file
Load Command
见 <mach-o/loader.h>
/*
* The segment load command indicates that a part of this file is to be
* mapped into the task's address space. The size of this segment in memory,
* vmsize, maybe equal to or larger than the amount to map from this file,
* filesize. The file is mapped starting at fileoff to the beginning of
* the segment in memory, vmaddr. The rest of the memory of the segment,
* if any, is allocated zero fill on demand. The segment's maximum virtual
* memory protection and initial virtual memory protection are specified
* by the maxprot and initprot fields. If the segment has sections then the
* section structures directly follow the segment command and their size is
* reflected in cmdsize.
*/
struct segment_command { /* for 32-bit architectures */
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_SEGMENT */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes sizeof section structs */
char segname[16]; /* segment name */
uint32_t vmaddr; /* memory address of this segment */
uint32_t vmsize; /* memory size of this segment */
uint32_t fileoff; /* file offset of this segment */
uint32_t filesize; /* amount to map from the file */
vm_prot_t maxprot; /* maximum VM protection */
vm_prot_t initprot; /* initial VM protection */
uint32_t nsects; /* number of sections in segment */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
/*
* The 64-bit segment load command indicates that a part of this file is to be
* mapped into a 64-bit task's address space. If the 64-bit segment has
* sections then section_64 structures directly follow the 64-bit segment
* command and their size is reflected in cmdsize.
*/
struct segment_command_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_SEGMENT_64 */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes sizeof section_64 structs */
char segname[16]; /* segment name */
uint64_t vmaddr; /* memory address of this segment */
uint64_t vmsize; /* memory size of this segment */
uint64_t fileoff; /* file offset of this segment */
uint64_t filesize; /* amount to map from the file */
vm_prot_t maxprot; /* maximum VM protection */
vm_prot_t initprot; /* initial VM protection */
uint32_t nsects; /* number of sections in segment */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
其中比较重要的
cmd表明Load Command类型 见<mach-o/loader.h>/* Constants for the cmd field of all load commands, the type */ 下面的宏定义vmaddr虚拟内存地址, 不是真正的内存地址, 因为 ALSR,使得进程中获取真正的地址 =vm address + slidevmsize段的虚拟内存大小fileoff段在文件的偏移filesize段在文件的大小
cmd 比较重要的有
LC_SEGMENT需要区分不同的架构. fishhook 用LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT重新定义了一下
#define LC_SEGMENT_64 0x19 /* 64-bit segment of this file to be
mapped */ 定义于 segment_command_64
#define LC_SEGMENT 0x1 /* segment of this file to be mapped */ 定义于 segment_command
后面会用这个字段来查询我们想要的 链接表, 符号表, 动态符号表, 具体的后面有代码和配图
Segment
segment 称为段,是链接器根据目标文件中属性相同(比如权限)的多个section 合并后的 section 集合.
__TEXT 只读区域 ,包括 macho header . load commands 和 一些 Section , 这部分可读可执行. 即 VM_PROT_READ(读)、VM_PROT_EXECUTE(执行)
__DATA 数据区可读可写, 即 VM_PROT_READ(读) VM_PROT_WRITE(写) VM_PROT_EXECUTE(可执行)
__LINKEDIT 链接器相关信息区域
fishhook 进行 hook 的关键是处理 __DATA 中的 __la_symbol_ptr 或者 __nl_symbol_ptr 这两个函数指针表的数据, 也只有这里面的数据,才能实现hook功能, 里面没有的, fishhook就无法做到, hook过程 后面会进行介绍
段相关信息摘录如下:
/*
* The names of segments and sections in them are mostly meaningless to the
* link-editor. 这里表明对于链接器而言 段名和
* But there are few things to support traditional UNIX
* executables that require the link-editor and assembler to use some names
* agreed upon by convention.
*
* The initial protection of the "__TEXT" segment has write protection turned
* off (not writeable). "__TEXT" 不可读
*
* The link-editor will allocate common symbols at the end of the "__common"
* section in the "__DATA" segment. It will create the section and segment
* if needed.
*/
/* The currently known segment names and the section names in those segments */
#define SEG_PAGEZERO "__PAGEZERO" /* the pagezero segment which has no */
/* protections and catches NULL 捕获空指针的段 */
/* references for MH_EXECUTE files */
#define SEG_TEXT "__TEXT" /* the tradition UNIX text segment 传统UNIX代码段 */
#define SECT_TEXT "__text" /* the real text part of the text */
/* section no headers, and no padding */
#define SECT_FVMLIB_INIT0 "__fvmlib_init0" /* the fvmlib initialization */
/* section */
#define SECT_FVMLIB_INIT1 "__fvmlib_init1" /* the section following the */
/* fvmlib initialization */
/* section */
#define SEG_DATA "__DATA" /* the tradition UNIX data segment 传统UNIX数据段*/
#define SECT_DATA "__data" /* the real initialized data section */
/* no padding, no bss overlap */
#define SECT_BSS "__bss" /* the real uninitialized data section 未初始化数据比如未初始化的全局变量*/
/* no padding */
#define SECT_COMMON "__common" /* the section common symbols are */
/* allocated in by the link editor */
#define SEG_OBJC "__OBJC" /* objective-C runtime segment OC运行时类信息部分*/
#define SECT_OBJC_SYMBOLS "__symbol_table" /* symbol table 符号表*/
#define SECT_OBJC_MODULES "__module_info" /* module information 模块信息*/
#define SECT_OBJC_STRINGS "__selector_strs" /* string table 字符串表*/
#define SECT_OBJC_REFS "__selector_refs" /* string table 字符串表*/
#define SEG_ICON "__ICON" /* the icon segment */
#define SECT_ICON_HEADER "__header" /* the icon headers */
#define SECT_ICON_TIFF "__tiff" /* the icons in tiff format */
#define SEG_LINKEDIT "__LINKEDIT" /* the segment containing all structs */
/* created and maintained by the link */
/* editor. Created with -seglinkedit */
/* option to ld(1) for MH_EXECUTE and */
/* FVMLIB file types only */
#define SEG_UNIXSTACK "__UNIXSTACK" /* the unix stack segment */
#define SEG_IMPORT "__IMPORT" /* the segment for the self (dyld) */
/* modifing code stubs that has read, */
/* write and execute permissions */
如何查询 Section 的读写权限
/**
* 查询该Section的读写权限
*
*/
static vm_prot_t get_protection(void *sectionStart)
{
mach_port_t task = mach_task_self();
vm_size_t size = 0;
vm_address_t address = (vm_address_t)sectionStart;
memory_object_name_t object;
#if __LP64__
mach_msg_type_number_t count = VM_REGION_BASIC_INFO_COUNT_64;
vm_region_basic_info_data_64_t info;
kern_return_t info_ret = vm_region_64(
task, &address, &size, VM_REGION_BASIC_INFO_64, (vm_region_info_64_t)&info, &count, &object);
#else
mach_msg_type_number_t count = VM_REGION_BASIC_INFO_COUNT;
vm_region_basic_info_data_t info;
kern_return_t info_ret = vm_region(task, &address, &size, VM_REGION_BASIC_INFO, (vm_region_info_t)&info, &count, &object);
#endif
if (info_ret == KERN_SUCCESS)
{
return info.protection;
}
else
{
return VM_PROT_READ;
}
}
Section
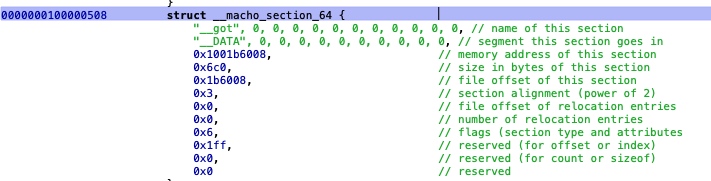
struct section_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
char sectname[16]; /* name of this section */
char segname[16]; /* segment this section goes in */
uint64_t addr; /* memory address of this section */
uint64_t size; /* size in bytes of this section */
uint32_t offset; /* file offset of this section */
uint32_t align; /* section alignment (power of 2) */
uint32_t reloff; /* file offset of relocation entries */
uint32_t nreloc; /* number of relocation entries */
uint32_t flags; /* flags (section type and attributes)*/
uint32_t reserved1; /* reserved (for offset or index) */
uint32_t reserved2; /* reserved (for count or sizeof) */
uint32_t reserved3; /* reserved */
};
sectname为Section的名称 比如__la_symbol_ptrsegname为Section所在的Segment名称 ,比如__DATAsize内存长度, 多少bytesoffset文件偏移, 和内存地址无法, 属于文件内部的偏移计算数值reserved1页偏移, 比较重要
对于 Section 来说, 对hook来将,比较重要的
__TEXT.__stubs桩代码__TEXT.__stub_helper绑定懒加载符号真正地址的功能代码,__la_symbol_ptr初始化的时候,指向__stub_helper__DATA.__la_symbol_ptr可执行文件使用的未定义符号, 懒加载的符号指针表, 没有绑定符号地址, 首次调用的时候会先掉经过__DATA.__stub_helper处理查询真正的符号地址并进行 懒加载符号的地址绑定 , fishhook后面会用到__DATA.__nl_symbol_ptr可执行文件使用的未定义符号, 未懒加载的符号指针表, 意味着链接时已经对符号进行的重定位, 绑定了符号与符号地址, fishhook后面会用到__DATA.__got代码段对数据型符号的引用,指向__got与上面__la_symbol_ptr与__nl_symbol_ptr函数符号类似- 当然对于 OC来讲有
__DATA.__objc_classlist类列表__DATA.__objc_classrefs被引用到的类列表, 经常用这两个对比来去除无用文件 - 小知识点:
__DATA.__objc_nlclslist没有加载的类列表,__DATA.__objc_nlcatlist没有懒加载的 分类列表, 在应用启动的时候会进行初始化+ load方法 , APM 可以对这部分进行耗时统计 - 未定义符号: 在读取了所有输入文件并完成了所有符号解析后,链接编辑器将搜索内部符号表,以查找尚未绑定到符号定义的任何符号引用。这些符号引用称为未定义符号。未定义符号对链接编辑过程的影响因要生成的输出文件类型以及符号类型而异。
mach-o header -> load command -> section
上面的这三部分, fishhook 能根据这部分做什么呢, 下面是实现代码部分
/**
* 重新绑定符号的过程
* rebindings 所有的hook替换方法链表
* header mach-o 文件头
* slide 基础偏移地址
*
*/
static void rebind_symbols_for_image(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings,
const struct mach_header *header,
intptr_t slide)
{
Dl_info info;
if (dladdr(header, &info) == 0)
{
return;
}
segment_command_t *cur_seg_cmd;
segment_command_t *linkedit_segment = NULL;
struct symtab_command *symtab_cmd = NULL;
struct dysymtab_command *dysymtab_cmd = NULL;
/**
*
* LC_SYMTAB这个LoadCommand主要提供了两个信息
* Symbol Table的偏移量与Symbol Table中元素的个数
* String Table的偏移量与String Table的长度
* LC_DYSYMTAB
* 提供了动态符号表的位移和元素个数,还有一些其他的表格索引
* LC_SEGMENT.__LINKEDIT
* 含有为动态链接库使用的原始数据
*
*/
// 首个命令的地址,也就是header的结束地址
uintptr_t cur = (uintptr_t)header + sizeof(mach_header_t);
// 根据命令的大小做偏移, 某个命令的大小都不同
for (uint i = 0; i < header->ncmds; i++, cur += cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize)
{
// 取出 load command
cur_seg_cmd = (segment_command_t *)cur;
// 如果是 segment 的宏定义
if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT)
{
// 如果segment 名字是 `__LINKEDIT` 的话, 含有为动态链接库使用的原始数据, ,如符号,字符串和重定位的表的入口
if (strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_LINKEDIT) == 0)
{
linkedit_segment = cur_seg_cmd;
}
}
// link-edit stab symbol table info
// Symbol Table的偏移量与Symbol Table中元素的个数
// String Table的偏移量与String Table的长度
else if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SYMTAB)
{
symtab_cmd = (struct symtab_command *)cur_seg_cmd;
}
// 提供了dynamic symbol table 动态符号表的位移和元素个数,还有一些其他的表格索引
else if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_DYSYMTAB)
{
dysymtab_cmd = (struct dysymtab_command *)cur_seg_cmd;
}
}
if (!symtab_cmd || !dysymtab_cmd || !linkedit_segment ||
!dysymtab_cmd->nindirectsyms)
{
return;
}
// 基址 = __LINKEDIT.VM_Address - __LINK.File_Offset + silde的改变值
// Find base symbol/string table addresses 确定基地址
uintptr_t linkedit_base = (uintptr_t)slide + linkedit_segment->vmaddr - linkedit_segment->fileoff;
// 确定符号表的地址 = 基地址 + 符号表的偏移量, 其余的表基本也是如此计算
nlist_t *symtab = (nlist_t *)(linkedit_base + symtab_cmd->symoff);
// 确定字符串表的地址
char *strtab = (char *)(linkedit_base + symtab_cmd->stroff);
// 确定动态符号表的地址
// Get indirect symbol table (array of uint32_t indices into symbol table)
uint32_t *indirect_symtab = (uint32_t *)(linkedit_base + dysymtab_cmd->indirectsymoff);
// mach-O header的结束地址
cur = (uintptr_t)header + sizeof(mach_header_t);
// 遍历所有的command
for (uint i = 0; i < header->ncmds; i++, cur += cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize)
{
// 获取 load command
cur_seg_cmd = (segment_command_t *)cur;
// 是否是 segment
if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT)
{
// 如果不是 `__DATA` 段 且 也不是 `__DATA_CONST`的常量段, 则继续
if (strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_DATA) != 0 &&
strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_DATA_CONST) != 0)
{
continue;
}
// 遍历 segment, cur_seg_cmd->nsects: 此segment的 section 数量
for (uint j = 0; j < cur_seg_cmd->nsects; j++)
{
//获取当前的Section
section_t *sect =
(section_t *)(cur + sizeof(segment_command_t)) + j;
// 查询 Section的类型, 如果是 `__la_symbol_ptr` 类型的. 绑定该部分
// 该部分符号会在该符号被第一次调用时,通过 dyld 中的 dyld_stub_binder 过程来进行加载
if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS)
{
// 则执行真正绑定过程
perform_rebinding_with_section(rebindings, sect, slide, symtab, strtab, indirect_symtab);
}
// 查询 Section的类型, 如果是 `__nl_symbol_ptr` 类型的. 绑定该部分
// non-lazy 符号是在动态链接库绑定的时候进行加载的
if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS)
{
perform_rebinding_with_section(rebindings, sect, slide, symtab, strtab, indirect_symtab);
}
}
}
}
}
先放配图
整个过程是
- 根据
mach_header_t能确认 首个Load Command的地址, 然后根据mach_header_t记录的ncmds能确认Load Command的数量, 这样就可以遍历Load Command找到需要的linkedit_segment,symtab_cmd,dysymtab_cmd如果没有找到就不需要继续了, 这个镜像不可能有对应的函数 linkedit_segment用处很简单, 就是找到 链接信息__LINKEDITSegment的首地址linkedit_base. 因为我们的symtab和dysymtab就在这个 Segment 中存储着. ps: 代码中 起linkedit_segment这个名字有问题, 因为它是一个 ``Load Command, 应该叫linkedit_cmd` 才对symtab_cmd,dysymtab_cmd记录着symtab和dysymtab相对__LINKEDITSegment 的偏移, 通过上一部得到的linkedit_base就可以计算出对应的真正内存首地址了- 然后是遍历所有的
Section, 根据flags与上SECTION_TYPE, 找到真正的函数调用指针表,S_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS对应的(__la_symbol_ptr)懒加载符号表,S_NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS对应的(__nl_symbol_ptr)非懒加载符号表 , 后面会仔细介绍.
fishhook 函数调用相关表
要认清这部分,首先要了解的是指针的概念, 破除奥秘的前提是理解指针.
- 指针
- 指针的地址
- 指针的值
/**
* 1. rebindings 需要替换的符号记录数组, 里面记录了 目标函数的名称,目标函数的签名, fake函数
* 2. section 为 `__la_symbol_ptr` 的section 或者 `__nl_symbol_ptr` 的section (因为这里的函数才可以被动态库加载,并映射到真正函数地址,这里存储的是指针表,也就是外部存储这里的指针,然后获取指针对应的值, 这个值就是真正的函数地址),也就是说这里只有符号的地址,没有符号的名称, 外部要hook目标函数,虽然终点在这里,但是无法一次找到,只能经过查询符号名称的间接过程来确认这个目标指针在哪里!!
* 3. slide 镜像的基地址偏移量 (基于内存保护的ALSR 技术产生的 随机偏移量), 后续的外部函数地址都会因此而改变
* 4. symtab 符号表 包含所有的符号信息(不包含名称, 名称需要从字符串表中查询), 不包含动态库的真正函数地址
* 5. strtab 字符串表 包含所有的符号名称,也只是名称
* 6. indirect_symtab 间接符号表 (包含了动态库加载时的 `__la_symbol_ptr`符号与`__nl_symbol_ptr`符号 got符号 以及其他符号) 在其对应符号表中的 **索引** , 仅仅是索引
*/
static void perform_rebinding_with_section(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings,
section_t *section,
intptr_t slide,
nlist_t *symtab,
char *strtab,
uint32_t *indirect_symtab)
这里说fishhook的相关表的汇总或者说概览, 下面具体说明相关表
__nl_symbol_ptr
- 位于
__DATA区 __nl_symbol_ptr非懒加载的符号指针表 (注意不是符号表,仅仅是指针), 在动态库load的时候就会将这部分外部符号与真正的虚拟地址进行映射
void func1 (int) {
// do something
}
/// `p` 就是符号指针 它不是函数本身
void(*p)(int) = &func1;
// 但是可以获取函数指针的值, 也就是真正函数的地址,然后调用函数
(*p)(20);
而 __nl_symbol_ptr 或者 下面的 __la_symbol_ptr 做的就是这件事情, 用这个临时的内存区域,存储动态库中对外的函数符号真正的调用地址.
那么在代码区 __TEXT 的汇编代码中,就可以一直存储这个临时的函数指针的地址, 不论 ALSR 如何偏移,改变镜像运行的真正内存地址, 代码区的这个临时函数指针不需要改变, 只要加载的时候将这个临时的函数指针表中对应函数的真正地址给修正好就可以.
__nl_symbol_ptr 这个函数指针表,是在镜像加载的时候,立马就被修正的, 里面存储的函数地址是正确的,真正的函数地址. 主要是因为这些函数会被镜像运行时立即调用. 没有延迟绑定的必要.
以名片举个栗子, 获取马云大大名片 p , 然后查询名片的内容 *p, 里面存储的是马云大大的地址. 名片就是这个临时的函数符号表. 我们可以随意的改变名片的内容, 比如让名片的内容存储我的地址(当然这是假地址), 找到我的地址后,我也可以再给一个真正的马云大大的地址. 这就是hook的真谛.
不过找名片的过程也很麻烦, 就好像你有一堆银行卡,你只知道要找建设银行卡, 你肯定不能立马获取,而是找到所有的卡,然后一个一个遍历,比对银行卡的名称,是不是建设银行卡. 符号的查找过程和这个类似,不过因为存储的数据结构问题,比这个过程更复杂一些.
__la_symbol_ptr
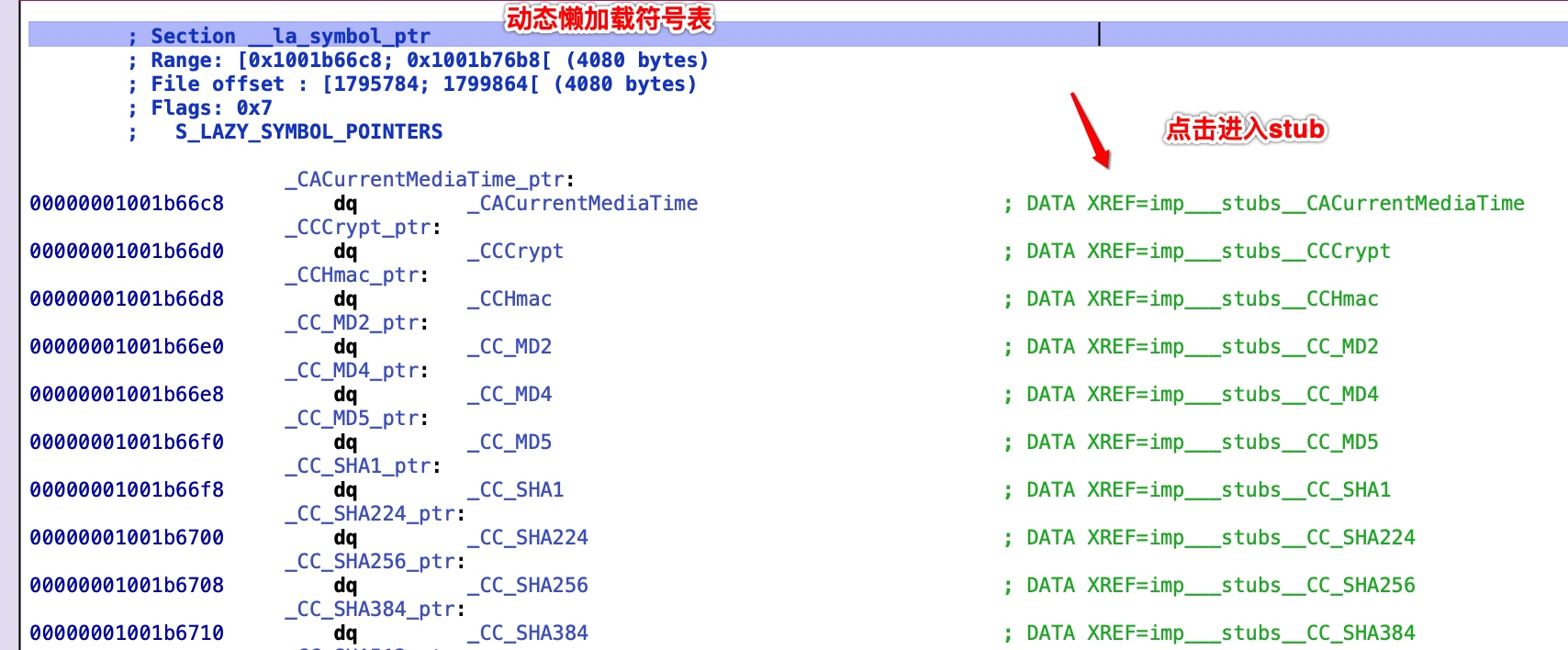
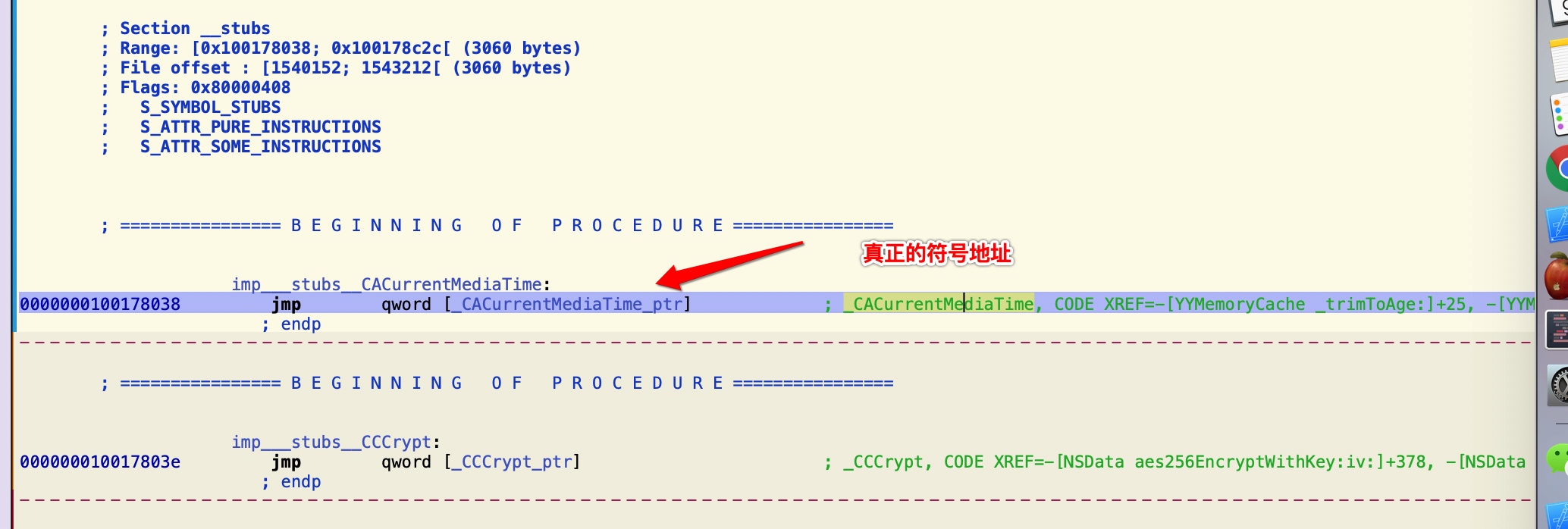
- 位于
__DATA区 __la_symbol_ptr懒加载的符号指针表,其数据在动态库镜像load的时候会被bind成dyld_stub_helper, 这个函数是一段寻找真正函数真正调用地址的代码- 在函数第一次是用到的时候,
dyld_stub_helper会被调用,找到真正函数调用地址时,会将__la_symbol_ptr对应的符号指针的值 替换为其真正的符号调用地址值 !!! - 懒加载是为了解决类似动态链接下对于全局和静态的数据访问都要进行复杂的GOT定位, 然后间接寻址的问题, 提升链接效率
- 比如很多符号可能不会被用到, 如果在动态库加载的时候再进行绑定函数地址的话,那么就会使得应用的启动速度降低.
注意: __la_symbol_ptr 和 __nl_symbol_ptr 指针表是动态库的能被外界 看到 并且 使用到 的外部符号 , 如果没有使用到,也不会在这个表中, 如果不能被看到也不会被添加到这两个表中.
控制可见性
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) // 符号可被外部链接
__attribute__((visibility("hidden"))) // 符号无法被外部链接, 如果外部使用到,则会报编译错误
对于我们程序里的静态库而言, 它仅仅是一个中间产物,最终仍然要被链接到最终的可执行文件中去,所以其使用到的符号一般被称为内部符号, 最终链接的时候会直接使用真正的符号地址,而不会再通过一个间接的符号指针进行处理. 相当于写死了调用. 而也就是因为静态库的符号又不会被外部的动态库调用, 所以很明显其符号不会被添加到 __la_symbol_ptr 和 __nl_symbol_ptr 中, 这个也是 fishhook 无法做到内部符号 hook 的原因了.
如果想处理内部符号的话,暂时我不太清除, 除了将静态库做成动态库处理, 比如使用 Cocoapods 的话 就打开 use_frameworks 来生成动态库 , 还能怎么做.
对于静态库的符号来说,先说最终结论 生产环境上, 建议直接去除所有符号, 动态库去除除了 Global Symbols 部分的其他符号, 这样别人就无法查看到静态库调用堆栈中符号的名称信息了. 自己查询的话,可以使用 生成的 dsym 文件. 当然 Xcode 默认是 将 Strip Style 设置 为 All Symbol 的.
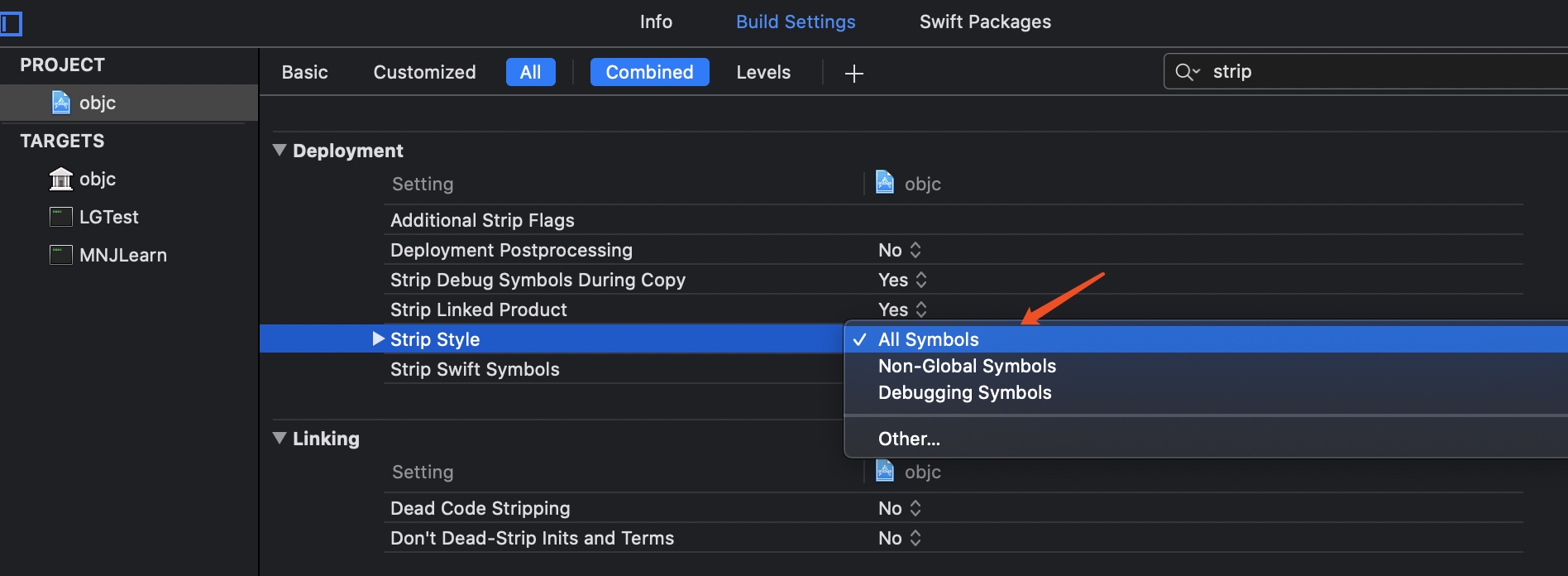
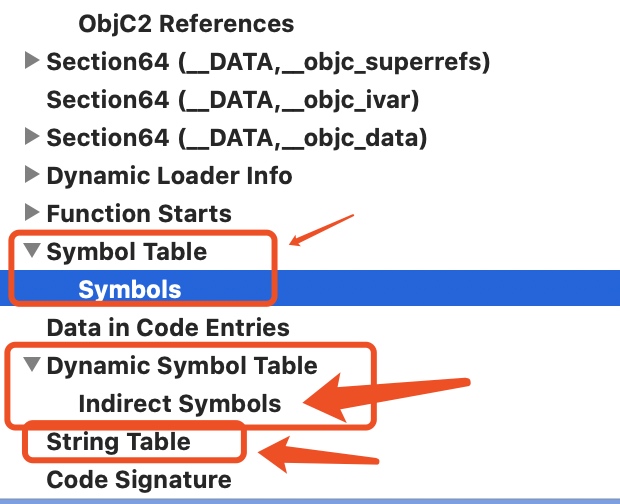
Indirect Symbol Table 或者 Dynamic Symbol Table / DST
An indirect symbol table entry is simply a 32bit index into the symbol tableto the symbol that the pointer or stub is refering to. Unless it is for a non-lazy symbol pointer section for a defined symbol which strip(1) as removed. In which case it has the value INDIRECT_SYMBOL_LOCAL. If the symbol was also absolute INDIRECT_SYMBOL_ABS is or'ed with that.
Dynamic Symbol Table 动态符号(间接符号表)表:
- 间接符号表中的 元素 是一个
uint32_t32位大小的偏移量值,指针的值 是对应元素n_list所代表的符号在符号表中的索引位置. - 保存与动态链接相关的导入导出符号, 比如
__la_symbol_ptr或者__nl_symbol_ptr的符号信息 (仅仅是对应符号表下标的信息), 不包括模块内部的符号. - 该表在 dyld 时期使用,并且在对象被加载的时候映射到进程的地址空间。所以我们可以说 DST 是符号表的子集
符号表
符号表: 保存所有符号, 比如 __la_symbol_ptr或者 __nl_symbol_ptr 中的符号和本地符号等. 其只是对debug有用。strip会去除符号表, 对这句话没有求证
/*
* This is the symbol table entry structure for 64-bit architectures.
*/
struct nlist_64 {
union {
uint32_t n_strx; /* index into the string table */
} n_un;
uint8_t n_type; /* type flag, see below */
uint8_t n_sect; /* section number or NO_SECT */
uint16_t n_desc; /* see <mach-o/stab.h> */
uint64_t n_value; /* value of this symbol (or stab offset) */
};
n_strx对应的是符号表的索引值, 可以根据索引和符号表的内存偏移量找到具体的符号名称, 用于对比我们查找的目标符号, 也就是类似上面讲的 建设银行卡.
重点: 其仅仅记录了 符号在 字符串表中的对应偏移量
n_strx,真正的符号名称 还是需要去 字符串表进行查询, 我们经常要对比目标符号是不是我们想要需要替换的符号,则需要先 遍历符号表,然后再去字符串表获取真正的符号名称, 这样才能真正达到我们的目的.
字符串表 .strtab / string table
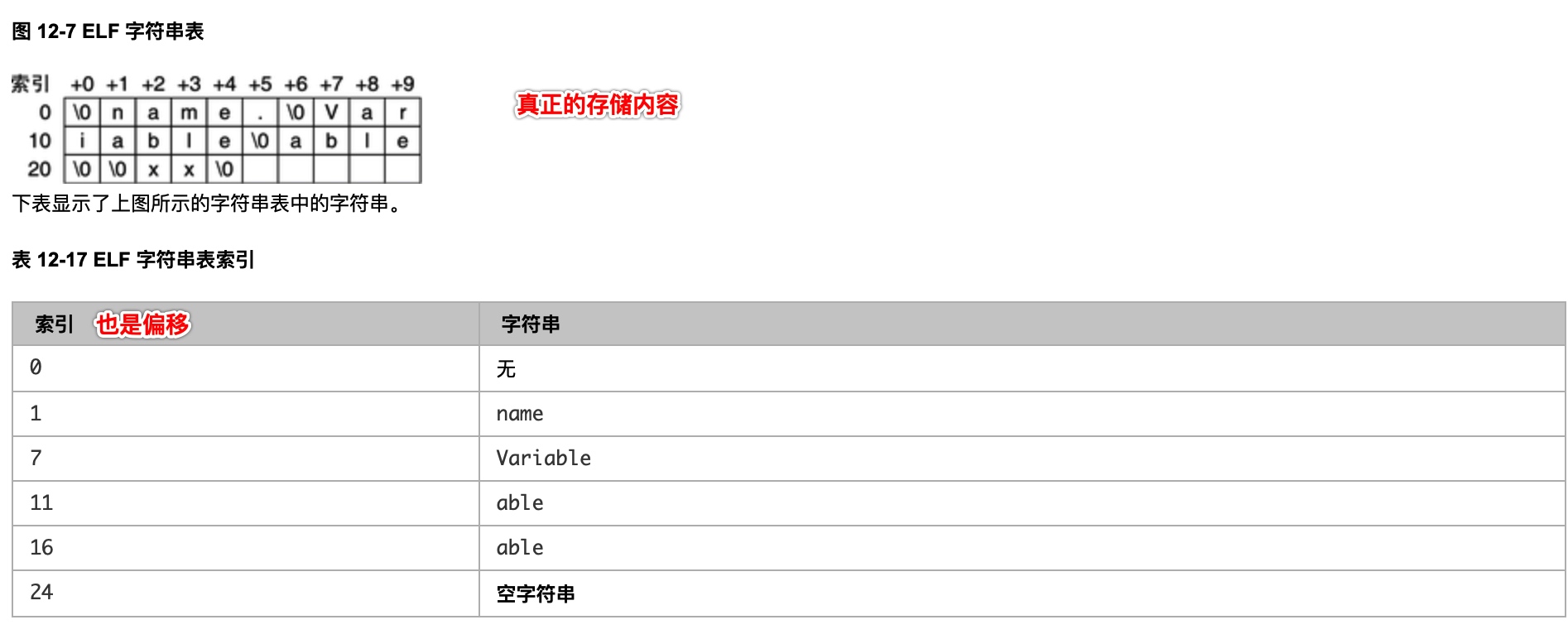
摘自字符串表节
可执行文件中所有的符号名称或者段名称等信息, 因为字符串的长度不固定, 所以无法用固定的结构表示它, 常见的做法是: 将字符串集中存储到一个表中, 然后使用字符串在表中的偏移来引用字符串.
问题: 如何知道符号表中某个符号的长度, 答符号表存储的字符以 \0 结尾
具体的真正绑定的过程
static void perform_rebinding_with_section(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings,
section_t *section,
intptr_t slide,
nlist_t *symtab,
char *strtab,
uint32_t *indirect_symtab)
{
// 判断是否是 `__DATA_CONST` 常量区
const bool isDataConst = strcmp(section->segname, "__DATA_CONST") == 0;
// indirect_symtab 间接符号表地址 ; reserved1 保留字段 , 表示 reserved (for offset or index) 用于描述 `__la_symbol_ptr`或者 `__nl_symbol_ptr` 在 `indirect_symtab`表中的起始地址.
// indirect_symbol_indices = 动态符号表 + 偏移量, 注意 indirect_symbol_indices 仅仅用于寻找 符号表 中的对应符号 n_list 结构体元素的下标 ; uint32_t symtab_index = indirect_symbol_indices[i];
uint32_t *indirect_symbol_indices = indirect_symtab + section->reserved1;
// indirect_symbol_bindings 这个是指的 `__la_symbol_ptr` or `__nl_symbol_ptr`表, 不要因为命名以为是间接符号表
// 它的首地址 = slide(基础偏移地址) + Section的内存相对地址 (memory address of this section)
// 已知其 value 是一个指针类型,整段区域用二阶指针来获取, 这个是 `__la_symbol_ptr` or `__nl_symbol_ptr`, 真正保存符号的调用地址 的地方 重要!!!!!!!!!
void **indirect_symbol_bindings = (void **)((uintptr_t)slide + section->addr);
// symtab 符号表是为了查找符号对应在 字符串表对应符号的 偏移地址
// 可读
vm_prot_t oldProtection = VM_PROT_READ;
if (isDataConst)
{
// 如果是常量区,查询权限
oldProtection = get_protection(rebindings);
// 让section可读写, 便于我们修改函数地址等数据
mprotect(indirect_symbol_bindings, section->size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE);
}
// 偏移的时候 使用 `size / sizeof(void *)` 为一个单位( 地址单位的大小, 保存的是地址)
for (uint i = 0; i < section->size / sizeof(void *); i++)
{
// indirect_symbol_indices为间接符号表中 `__la_symbol_ptr` 或者 `__nl_symbol_ptr` 符号数组(元素为uint32_t)的首地址,其长度为Section的地址数组长度, 所以我们可以根据 section 指针数组长度进行 indirect_symbol_indices的遍历
uint32_t symtab_index = indirect_symbol_indices[i];
/*
* An indirect symbol table entry is simply a 32bit index into the symbol table
* to the symbol that the pointer or stub is refering to. Unless it is for a
* non-lazy symbol pointer section for a defined symbol which strip(1) as
* removed. In which case it has the value INDIRECT_SYMBOL_LOCAL. If the
* symbol was also absolute INDIRECT_SYMBOL_ABS is or'ed with that.
*/
// 如果是 abs 或者 是 本地 则跳过 (因为不是动态库的外部符号)
if (symtab_index == INDIRECT_SYMBOL_ABS || symtab_index == INDIRECT_SYMBOL_LOCAL ||
symtab_index == (INDIRECT_SYMBOL_LOCAL | INDIRECT_SYMBOL_ABS))
{
continue;
}
// 该下标符号表元素是 nlist_64 结构, 查找里面的 index into the string table ,也就是 n_strx
uint32_t strtab_offset = symtab[symtab_index].n_un.n_strx;
// 获取符号名称
char *symbol_name = strtab + strtab_offset;
// C 语言的默认调用惯例 Calling Convention (cdecl) 中 名字修饰策略, 直接在函数名称前加1个下划线!!! 所以下面对比符号的时候 会从 symbol_name[1] 开始, 去掉了 symbol_name[0] 的 '_'
bool symbol_name_longer_than_1 = symbol_name[0] && symbol_name[1];
// 遍历所有的hook符号链表
struct rebindings_entry *cur = rebindings;
while (cur)
{
for (uint j = 0; j < cur->rebindings_nel; j++)
{
// 当前符号是否和需要hook的原函数名称一致
if (symbol_name_longer_than_1 &&
strcmp(&symbol_name[1], cur->rebindings[j].name) == 0)
{
// 如果被hook函数的新函数地址 不同于 <<在 数据区 `__nl_symbol_ptr`或者`__la_symbol_ptr`>> 同名符号结构中的函数地址 , 则将hook函数链表中的原函数地址记录下来 (动态函数表的函数地址), 记录到链表中,供以后使用
if (cur->rebindings[j].replaced != NULL &&
indirect_symbol_bindings[i] != cur->rebindings[j].replacement)
{
*(cur->rebindings[j].replaced) = indirect_symbol_bindings[i];
}
// 并且将hook函数的新函数地址 更新到 `__nl_symbol_ptr`或者`__la_symbol_ptr` 中
indirect_symbol_bindings[i] = cur->rebindings[j].replacement;
goto symbol_loop; // 结束该内层的遍历, 查找下一个符号
}
}
cur = cur->next;
}
symbol_loop:;
}
// 恢复原来的内存权限改写
if (isDataConst)
{
int protection = 0;
if (oldProtection & VM_PROT_READ)
{
protection |= PROT_READ;
}
if (oldProtection & VM_PROT_WRITE)
{
protection |= PROT_WRITE;
}
if (oldProtection & VM_PROT_EXECUTE)
{
protection |= PROT_EXEC;
}
mprotect(indirect_symbol_bindings, section->size, protection);
}
}
fishhook 的应用
基于上面关于二进制文件,各组成部分的功能, fishhook 诞生了.
fishhook 文档中的查找过程
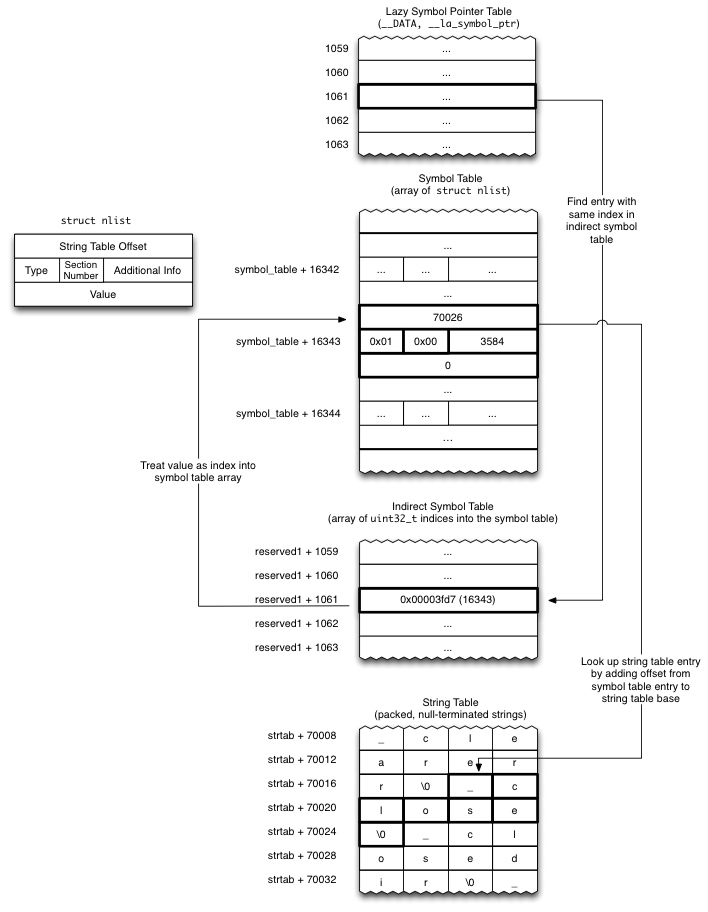
步骤一:
- 查找 记录
__LINKEDIT/LC_SYMTAB/LC_DYSYMTAB相关的3 个Command - 根据
__LINKEDIT和LC_SYMTAB/LC_DYSYMTAB计算出 字符串表,符号表和 动态符号表(间接符号表)共3个位置 - 因为我们真正的函数映射表
__nl_symbol_ptr和__la_symbol_ptr在__DATA段存在, 无法直接找到具体的目标函数位置,所以我们需要遍历所有的section, 根据section中 的flags字段, 来确定其是否是__nl_symbol_ptr或者__la_symbol_ptr的Section, 如果找到将会对其进行解析.
步骤二:
- 这部分仅仅有符号指针信息,虽然最终目的是该这里的数据,但因为不包含符号名称,不确认修改的是那个符号指针的值, 所有要继续处理
__la_symbol_ptr或者__nl_symbol_ptr的Section,通过它的section->reserved1来确认 这部分临时符号指针表 在indirect_symbol间接符号表 所处的首地址位置. - 这部分间接符号表同样不包含符号名称, 所以需要继续遍历
indirect_symbol表中 归属__la_symbol_ptr或者__nl_symbol_ptr那部分数组信息, 然后根据这部分数组的元素获取 符号表 中对应元素nlist的索引 - 这部分符号表对应元素也不包含符号名称, 所以需要继续根据
Symbol Table-> 元素struct nlist包含以下内容, 根据其中的n_strx获取 字符串表 该符号的偏移量- String Table Offset
- Section Number
- Type
- Additional Info
- Value
- 终于终于能在这里
String Table定位其offset, 最终定位符号名称, 如果与想要替换的符号相同的话, 则更新之前当前懒加载符号或者非懒加载符号,当前符号指针的值, 也就是对应符号的函数地址值为 fake 函数地址
这里要注意的是, indirect_symbol_bindings的命名让人以为是间接符号表 indirect_symbol , 实际上它不是, 它是当前 section 也就是 __nl_symbol_ptr 或者 __la_symbol_ptr 符号指针表, 命名引起误解, 没办法.
indirect_symbol_bindings[i] = cur->rebindings[j].replacement;
其实步骤二本身就是在
for (uint i = 0; i < section->size / sizeof(void *); i++)
这个 for循环里面处理的, 枚举的就是 indirect_symbol_bindings中某一个符号, for循环里做这个多, 无非是因为, indirect_symbol_bindings 这个函数指针表里面没有符号名称, 否则哪里需要这么麻烦.
下面这个摘自 <<深入理解Symbol>>的图片可以直观的看到这个过程
问题
- 为什么需要将 动态库的外部符号 分在
__nl_symbol_ptr和__la_symbol_ptr两个表中, 不能都放在一个__la_symbol_ptr表 或者__nl_symbol_ptr表吗 ? - 动态库中的符号都在
__nl_symbol_ptr和__la_symbol_ptr表中记录吗? - 静态库的符号在哪里存储呢? fishhook 为什么不能 hook 静态库的符号?
- 如何 hook 静态库的符号呢
文中对这些都有一定的描述, 深入了解还是得看编译原理. 不过对于静态库的这部分,想 hook 我暂时还找不到好的方法. 好像 Dobby 这个库可以, 暂时没有研究过 https://github.com/jmpews/Dobby/issues/44
Discussion